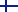
UV Dose, UV Disinfection Time and UV Spread Calculator
1. Before making calculations, it is necessary to determine the power of the UV source. To do this, look at the specification of the lamp.
For example, the power of the UV source is
16.4 μW/cm² for KVP-SM-20,
39.8 μW/cm² for KVP-SM-40, and
12.6 μW/cm² for KVP-FARUV-DLA-15.
2. To calculate UV Irradiance from a specific distance, enter its value in meters in the Distance field and click the Calculate UV Irradiance button.
3. To calculate the disinfection time, it is necessary to know the disinfection dose for a particular pathogen. You may find it in the UV IRRADIATION DOSAGE TABLE table below. Please note that the values in the table are in microjoules per square centimeter and are listed separately for 254 nm and 222 nm. Enter its value in the UV Dose field and click the Calculate Time button.
4. To calculate the UV dose for a particular time, enter the value in the Time field in seconds and click the Calculate Dose button.
5. You can also calculate the UV spread and coverage area by clicking the Calculate UV Spread button.
Note: The calculator does not work correctly at short distances less than the length of the lamp.
| A) Bacteria | Medium | Wavelength [nm] | Dose [mJ/cm²] | Ratio to 254 |
| Acinetobacter radioresistens | S | 222 | 16.43 | |
|
Arthrobacter nicotinovorans
|
L | 222 | 5.97 | 1.48 |
| 254 | 04.04 | |||
|
Bacillus cereus
|
L | 222 | 5.67 | 1.95 |
| 254 | 2.91 | |||
|
Bacillis subtilis
|
L | 222 | 04.09 | 0.97 |
| 254 | 4.22 | |||
|
Clostridium sporogenes
|
L | 222 | 2.87 | 0.61 |
| 254 | 4.69 | |||
|
Deinococcus radiodurans
|
L | 222 | 29.65 | 0.53 |
| 254 | 56.21 | |||
|
Enterococcus faecalis
|
L | 222 | 9.14 | 1.52 |
| 254 | 06.03 | |||
| S | 222 | 7.59 | ||
|
Escherichia coli
|
L | 222 | 2.10 | 1.22 |
| L | 230 | 3.67 | 2.13 | |
|
Escherichia coli
|
254 | 1.73 | ||
| S | 210 | 4.29 | 0.05 | |
| 222 | 63.56 | 0.69 | ||
| 254 | 92.24 | |||
|
Listeria monocytogenes
|
L | 222 | 3.58 | 0.41 |
| 254 | 8.70 | |||
| S | 222 | 145.65 | 55.25 | |
| 254 | 2.636 | |||
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
|
L | 222 | 1.98 | 2.47 |
| 254 | 0.80 | |||
|
Salmonella Typhimurium
|
L | 222 | 1.97 | 0.63 |
| 230 | 4.00 | 1.29 | ||
| 254 | 3.10 | |||
| S | 222 | 109.32 | 1.52 | |
| 254 | 71.86 | |||
|
Staphylococcus aureus
|
L | 222 | 324 | 1.33 |
| 254 | 2.43 | |||
| S | 210 | 19.71 | 4.20 | |
| 222 | 4.69 | 1.46 | ||
| 230 | 3.50 | 01.09 | ||
| 254 | 3.21 | |||
| Streptococcus pyogenes | L | 222 | 20.91 | |
|
Streptomyces griseus conidia
|
S | 210 | 56.18 | |
| 230 | 106.90 | |||
|
Yersinia enterocolytica
|
L | 222 | 2.20 | 1.49 |
| 254 | 1.48 | |||
| B) Bacterial spores | Medium | Wavelength [nm] | Dose [mJ/cm²] | Ratio to 254 |
|
Alicyclobacillus acidoterrestris spores
|
L | 222 | 06.02 | 0.71 |
| 254 | 8.50 | |||
|
Bacillus cereus
spores |
L | 222 | 17.88 | 0.39 |
| 254 | 46.42 | |||
|
Bacillus pumilus
spores |
L | 210 | 8.00 | 0.13 |
| 222 | 18.79 | 0.29 | ||
| 254 | 64.00 | |||
| S | 222 | 8.52 | ||
|
Bacillus subtilis
spores |
L | 210 | 13.96 | 0.97 |
| 222 | 6.34 | 0.44 | ||
| 230 | 10.75 | 0.75 | ||
|
Bacillus subtilis
spores |
254 | 14.37 | ||
| S | 210 | 8.57 | 4.80 | |
| 222 | 0.89 | 0.50 | ||
| 230 | 0.83 | 0.46 | ||
| 254 | 1.79 | |||
| Bacillus thuringiensis spores | L | 222 | 10.73 | |
|
Clostridioides diHicile spores
|
L | 222 | 13.23 | 0.73 |
| 254 | 18.02 | |||
| S | 222 | 16.67 | 0.17 | |
| 254 | 100.36 | |||
|
Clostridioides sporogenes spores
|
L | 222 | 10.37 | 0.76 |
| 254 | 13.64 | |||
|
Chlostridium pasteurianum spores
|
L | 222 | 2.63 | 1.18 |
| 254 | 2.23 | |||
|
Streptomyces griseus spores
|
L | 210 | 21.20 | 4.13 |
| 222 | 6.67 | 1.30 | ||
| 254 | 5.13 | |||
| S | 210 | 33.77 | 5.14 | |
| 222 | 14.38 | 2.19 | ||
| 230 | 15.33 | 2.33 | ||
| 254 | 6.57 | |||
|
Thermoactino- myces vulgaris spores
|
L | 222 | 15.14 | 0.40 |
| 254 | 38.17 | |||
| C) Fungi | Medium | Wavelength [nm] | Dose [mJ/cm²] | Ratio to 254 |
|
Apergillus niger
spores |
L | 222 | 106.82 | 0.88 |
| 254 | 121.97 | |||
|
Penicillium expansum spores
|
L | 222 | 13.82 | 0.84 |
| 254 | 16.50 | |||
|
Candida albicans
|
L | 222 | 9.82 | 01.02 |
| 254 | 9.67 | |||
|
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
|
L | 222 | 22.33 | 1.31 |
| 254 | 17.00 | |||
| S | 210 | 33.00 | 5.66 | |
| 222 | 12.77 | 2.19 | ||
| 254 | 5.836 | |||
|
Trichophyton rubrum spores
|
L | 222 | 13.64 | 1.58 |
| 254 | 8.63 | |||
| D) Viruses | Medium | Wavelength [nm] | Dose [mJ/cm²] | Ratio to 254 |
|
Adenovirus
|
L | 210 | 2.13 | 0.07 |
| 222 | 05.09 | 0.16 | ||
| 230 | 5.74 | 0.18 | ||
| 254 | 31.25 | |||
|
Bacillus mega- therium phage
|
S | 222 | 4.79 | 1.98 |
| 254 | 2.43 | |||
|
Encephalomyocarditis virus
|
L | 222 | 4.71 | 0.87 |
| 254 | 5.44 | |||
|
Feline calcivirus
|
L | 222 | 9.57 | 1.000 |
| 254 | 9.57 | |||
|
Herpes simplex virus
|
L | 222 | 0.96 | 0.25 |
| 254 | 3.90 | |||
| Human coronavirus | A | 222 | 0.48 | |
|
Influenza virus
|
L | 222 | 43.48 | 0.32 |
| 254 | 136.99 | |||
| A | 222 | 1.28 | 1.51 | |
| 254 | 0.85 | |||
|
Thermoactinomyces vulgaris spores
|
L | 222 | 15.14 | 0.40 |
| 254 | 38.17 | |||
| D) Viruses | Medium | Wavelength [nm] | Dose [mJ/cm²] | Ratio to 254 |
|
Adenovirus
|
L | 210 | 2.13 | 0.07 |
| 222 | 05.09 | 0.16 | ||
| 230 | 5.74 | 0.18 | ||
| 254 | 31.25 | |||
|
Bacillus mega- therium phage
|
S | 222 | 4.79 | 1.98 |
| 254 | 2.43 | |||
|
Encephalomyocarditis virus
|
L | 222 | 4.71 | 0.87 |
| 254 | 5.44 | |||
|
Feline calcivirus
|
L | 222 | 9.57 | 1.000 |
| 254 | 9.57 | |||
|
Herpes simplex virus
|
L | 222 | 0.96 | 0.25 |
| 254 | 3.90 | |||
| Human coronavirus | A | 222 | 0.48 | |
|
Influenza virus
|
L | 222 | 43.48 | 0.32 |
| 254 | 136.99 | |||
| A | 222 | 1.28 | 1.51 | |
| 254 | 0.85 | |||
|
Phage TI
|
S | 210 | 1.76 | 1.71 |
| 230 | 2.11 | 02.05 | ||
| 254 | 01.03 | |||
|
Phage T1UV
|
L | 210 | 1.67 | 0.39 |
| 222 | 2.84 | 0.67 | ||
| 230 | 5.00 | 1.17 | ||
| 254 | 4.27 | |||
|
Phage T2
|
L | 222 | 3.36 | 1.63 |
| 254 | 2.060 | |||
|
Phage T7
|
L | 210 | 1.21 | 0.56 |
| 222 | 1.72 | 0.80 | ||
| 230 | 3.52 | 1.64 | ||
| 254 | 2.15 | |||
|
Phage MS2
|
L | 210 | 6.76 | 0.35 |
| 222 | 835 | 0.43 | ||
| 230 | 15.38 | 0.79 | ||
| 254 | 19.45 | |||
|
Phage PhiX174
|
L | 222 | 1.84 | 1.73 |
| 230 | 2.2 | 02.07 | ||
| 254 | 01.06 | |||
|
Phage Qft
|
L | 210 | 3.20 | 8.67 |
| 222 | 5.12 | 13.86 | ||
| 230 | 10.67 | 28.91 | ||
| 254 | 0.37 | |||
|
Polyomavirus
|
L | 222 | 106.53 | 1.54 |
| 254 | 69 | |||
|
Reovirus 3
|
L | 222 | 3.30 | 0.28 |
| 254 | 11.96 | |||
|
Rotavirus
|
L | 222 | 4.55 | 0.41 |
| 254 | 11.11 | |||
| Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus | S | 222 | 1.20 | |
|
Staphylococcus aureus phage
|
230 | 14.33 | 1.79 | |
| 254 | ||||
|
Tulane virus
|
222 | 5.56 | 1.00 | |
| 254 | 5.56 | |||
|
Vaccinia virus
|
222 | 6.53 | 2.37 | |
| 254 | 2.76 | |||
| 230 | 3.00 | 2.25 | ||
| 254 | ||||
| Vesicular stomatitis virus | 222 | 1.12 | 01.06 | |
Please note that many variables (air flow, humidity, distance of microorganism to the UV light, irradiation time) take place in a real world environment that make actual calculating of the UV dosage very difficult. However, it is proven that UV light will kill any DNA-based microorganism given enough UV dosage. UV breaks down DNA on a cumulative basis. Therefore, as air circulates through the ductwork of an HVAC system containing an UV light, the UV light continuously disinfects the air. If a microorganism is not effectively deactivated on the first pass through the ductwork, the UV light will continue to break its DNA down on subsequent passes. Microorganisms do not sit in a static environment in HVAC systems except on coils which can be exposed to UV light also. Microorganisms multiply rapidly if not controlled. The UV light helps to reduce airborne microorganisms from the indoor environment.
The maximum permissible UV-C exposure shall not exceed the ACGIH TLV and NIOSH REL of 22.0 mJ/cm2 for an 8 h day, 40 h work week exposure to UV radiation.